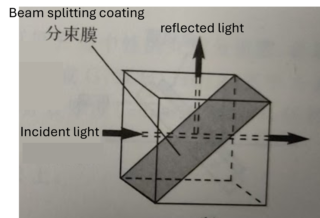
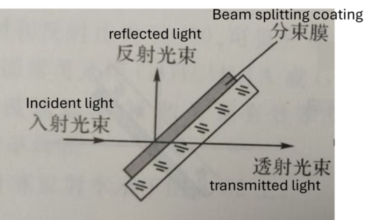
A beam splitter is an optical instrument that can split a beam of light into two beams by reflecting or transmitting light. It is an important component of many optical instruments (such as interferometers) and fiber-optic telecommunication equipment.
Light beam can be splitted by different ways. There are energy splitting, spectral splitting, and polarization splitting.
Energy splitting can split an incident light beam into beams of different energies. The most common ratio is 1:1 splitting, but there are also various energy ratios depending on the application. Spectral splitting splits the incident light into two beams with different spectral ranges. Polarization splitting can control the polarization difference of the split light beams.
A beam splitter is usually always used at an angle, which can easily separate the incident light into two parts: reflected light and transmitted light. If the reflected light and the transmitted light have different spectral components, or different colors, this type of beam splitter is usually called a dichroic mirror.
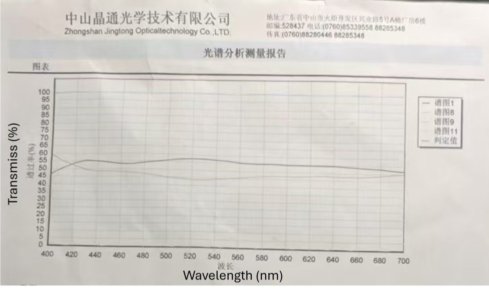
A neutral beam splitter is a commonly used beam splitter. It splits a beam of light into two beams with the same spectral components. It has the same transmittance and reflectance ratio for each wavelength in a certain wavelength region, such as the visible light region, so the reflected light and the transmitted light are neutral. Neutral spectroscopes with a transmittance and reflectance ratio of 50/50 are the most common.
Spectral spectroscopes are often used for color spectrometry (reflected light and transmitted light have different spectral ranges).